Crypto Bridging Explained
Crypto bridging allows the transfer of assets between blockchains. Our latest guide explains in detail what it entails and how it works.
Imagine a world where every country had its own distinct internet, isolated from everyone else. You can't access information or services outside your country's internet, limiting your opportunities. This scenario mirrors the early days of blockchain technology — isolated networks with limited interoperability. But then came the concept of crypto bridging, a technology breaking down these digital borders, allowing for the free movement of assets and information across multiple blockchains. In this guide, we'll journey through the ins and outs of crypto bridging, understand its mechanics, types, and real-world applications, and peek into the future of this transformative technology.
Key Takeaways
- Enhancing Interoperability: Crypto bridging connects isolated blockchains, enabling seamless asset and data transfers across diverse platforms.
- Types of Bridges: Bridges can be custodial (requiring trust in a third party) and non-custodial (trustless, with user control), each with unique trade-offs between ease of use and security.
- Practical Impact: Beyond financial transactions, crypto bridging expands possibilities in DeFi, NFT marketplaces, and cross-chain liquidity, transforming how users interact with digital assets.
- Future Prospects: While promising, crypto bridging faces challenges in security, scalability, and user experience, demanding ongoing innovation for mass adoption.
- Simplifying User Experience: Solutions like Ambire Wallet are pivotal in making crypto bridging more user-friendly, pushing for broader accessibility in the blockchain space.
Definition of crypto bridging
At its core, crypto bridging is a process that allows the transfer of assets and data from one blockchain to another. Think of it as a digital bridge connecting two islands, enabling people (or, in this case, assets and data) to move freely between them.
How crypto bridges work
Bridging between blockchains might seem complex, but it revolves around a simple principle: communication. Before delving into a real-world scenario, it's essential to understand that these bridges facilitate a conversation between two separate blockchains, allowing them to understand each other's transactions and records. Now, consider Ethereum and Bitcoin, two unique ecosystems. If you want to use your BTC within Ethereum's diverse DeFi world, a bridge accomplishes this. Your BTC is locked on the Bitcoin network, and an equivalent amount of WBTC is minted on Ethereum, mirroring its value and allowing you seamless interaction with Ethereum's native applications. This interoperability is achieved through smart contracts, ensuring the entire process is secure, transparent, and efficient.
Types of crypto bridges
In the blockchain space, not all bridges are built the same. They differ based on their operational structure and the level of trust required to use them. Let’s look at the different kinds:
- Centralized bridges are like traditional banks — efficient but controlled by a single entity. For instance, WBTC uses a system where BitGo, a cryptocurrency financial services provider, oversees the minting of WBTC tokens on Ethereum in exchange for an equal number of BTC tokens, which BitGo holds.
- Decentralized bridges operate without a central authority, offering a higher degree of trustlessness. ChainBridge, for example, allows you to move assets between different blockchains without relying on a central party, enhancing security and control for the user.
- Federated bridges are a hybrid, combining aspects of centralized and decentralized structures. The Liquid Network employs a federation of known, trusted entities, each participating in the operation and maintenance of the bridge, providing a balance between trustlessness and efficiency.
Let's examine a comparison table to better understand the differences between these bridges. It breaks down each type of bridge by speed, cost, security, and decentralization level, providing a clear, concise way to understand the trade-offs involved in each.
| Type | Speed | Cost | Security | Decentralization Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centralized | High | Low | Depends on the entity |
Low |
| Decentralized | Moderate | Moderate-High | High | High |
| Federated | High | Moderate | High | Moderate |
Atomic swaps
The concept of atomic swaps dates back to 2013 (even though, in reality, they didn’t gain practicality until 2017) - making them practically ancient technology in the history of the blockchain. So what are they? They simply allow peer-to-peer transactions between individuals holding different tokens on separate blockchains - without the need for any intermediaries.
Let’s look at an example: if you have ETH and want to swap it for BTC, you could use a centralized exchange to do so. They require registration, and you may even be asked to provide KYC. You would also need to transfer the ETH to the exchange, convert it to BTC, pay fees, and wait a while. Then, you need to withdraw the BTC to a Bitcoin wallet. This does sound quite complicated and lengthy, though, doesn’t it? This is where atomic swaps can come in and solve many challenges.
We can even say that to this day, atomic swaps are possibly the only way to have a truly decentralized bridge, and they help to foster a true DeFi ethos. There are projects out there working towards achieving this, e.g. Atomic Cloak, an account abstraction project that was presented at ETH Prague in June 2023:
1/3 Two account abstraction projects from @EthPrague just blew me away:
— Ivo (@Ivshti) June 12, 2023
- QR Seal, a privacy-preserving, gas-efficient multisig
- Atomic Cloak, a mixer and cross-chain bridge in one
Incidently both use Schnorr signatures
More below:
Real-world applications and benefits
The advent of crypto bridging marks a paradigm shift in interacting with blockchains. But what does this mean for the average user?
Firstly, it democratizes access to DeFi products. Using crypto bridges, you can take Bitcoin, originally confined to its native blockchain, and participate in Ethereum's thriving DeFi ecosystem through a representation like WBTC. This process significantly expands your potential to earn interest on your assets and engage with innovative financial products.
Furthermore, it revolutionizes the NFT marketplaces. Artists can create work on one blockchain and sell it on another — for example, mint an NFT on Ethereum but sell it on the Binance Smart Chain — thereby accessing a broader market and ensuring the best possible sale conditions. For liquidity providers, it's a game-changer. They can move their assets across chains, participate in various liquidity pools, and optimize their yield strategies like never before.
However, it's not a silver bullet. The ecosystem grapples with challenges like smart contract vulnerabilities, scaling issues, and the complexity of maintaining decentralization without compromising on speed and efficiency.
Ambire Wallet and cross-chain transfers
Navigating the world of crypto bridging doesn't have to be difficult or daunting, thanks to solutions like Ambire Wallet. Amongst its other cool features, it is designed to make cross-chain transfers a breeze. For example, if you want to transfer USDT from Ethereum to the Binance Smart Chain or ETH from Ethereum to Optimism, it's a straightforward process with Ambire Wallet, no different than a standard token transfer on a single chain. This ease of use starkly contrasts the often complex and time-consuming process of manual cross-chain transfers, which require understanding both networks involved, transaction fees, and bridge interfaces.
All you need to do is go to Cross-Chain in the wallet menu. There, you choose the token (and the amount) you’d like to bridge from the currently selected network and decide to which network (and even which currency) you’d like to transfer to:
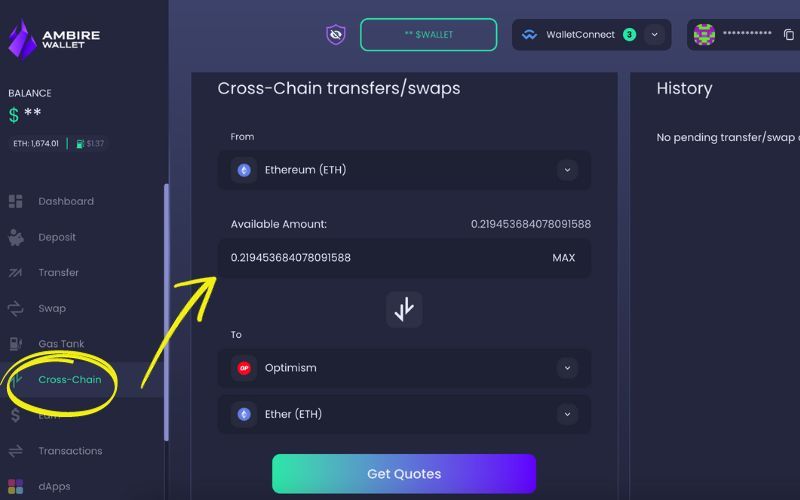
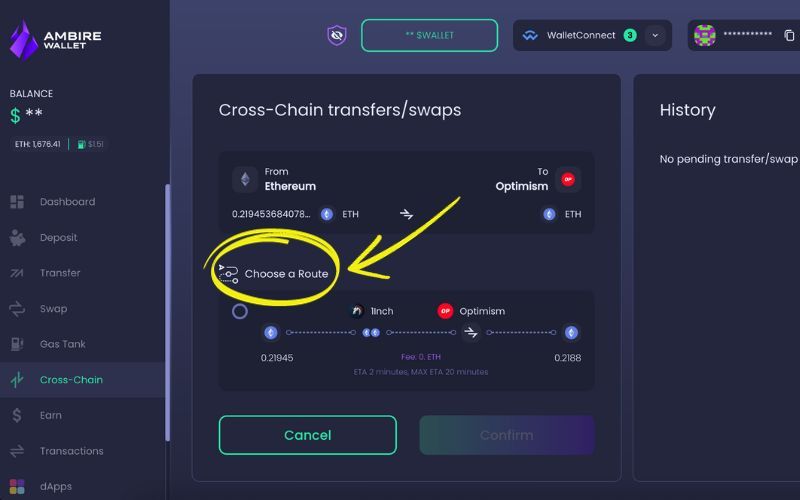
When you click on Get Quotes, you will see the available options (sometimes it may just be one, but if it’s a popular token, you may get more). You just need to select your preferred route and click on Confirm, after which you’ll be prompted to sign the transaction and complete the transfer. And that’s it! Your crypto will be bridged once the transaction is successful.
The future of crypto bridging
Crypto bridging is poised for exponential growth, but several hurdles must first be overcome. Security is paramount; the ecosystem needs robust solutions to smart contract vulnerabilities to prevent exploits and loss of funds. Scalability is another issue; as more users embrace crypto, the bridges must handle a higher volume of transactions without leading to congested networks and exorbitant fees.
Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos are pioneering the interoperability front, working on solutions that allow seamless interaction between blockchains. These innovations are crucial for mass adoption, as they'll provide the infrastructure necessary for a fully interoperable blockchain ecosystem capable of supporting a global user base. It is worth noting that Ethereum 2.0 originally planned to introduce sharding (or splitting up the main blockchain into separate segments, so nodes only need to verify a subset of transactions) & seamless communication between the shards. This means that as the nodes validate transactions in parallel, dApps can scale to accommodate more users because the network throughput can increase.
Not everything is bleak though, don’t worry. Recently, there has been talk about enshrining features into the Ethereum protocol. But what does this mean? Simply put, it means integrating (or natively implementing) new features directly into the core code of a blockchain protocol. Vitalik Buterin (Ethereum's Co-Founder) has suggested that more could be achieved on the blockchain to improve scalability and help with digital asset exchange, increase privacy & account safety, reduce costs, etc. You can read more about enshrining (and Vitalik’s opinion of it) here:
Should Ethereum be okay with enshrining more things in the protocol?https://t.co/7F7yOLBoUr
— vitalik.eth (@VitalikButerin) September 30, 2023
Conclusion
In conclusion, crypto bridging is more than a technological innovation; it's the key to unlocking the full potential of the blockchain universe. It stands at the center of a future where these digital ecosystems can communicate, collaborate, and evolve together. While challenges remain, the progress so far is promising, signaling a future where these digital bridges lead to a world of unexplored opportunities. As we stand on the precipice of this new era, one thing is clear: the bridges we build today will pave the way for the interconnected digital economies of tomorrow.
Related articles
Layer 1 vs. Layer 2 vs. Layer 3 Blockchains Explained
Transaction Batching 101, or How to Streamline Crypto Transactions
Understanding Token Approvals: Benefits, Risks and Best Practices
Interested in Ambire? Follow us:
Discord | X (Twitter) | Reddit | GitHub | Telegram | Facebook
